NVH
BACKGROUND
The comfort and light-weight requirements of vehicles are constantly increasing, however, both specifications work against each other. Reducing the weight of modern cars often times makes them more susceptible of experiencing undesired vibrations. Therefore, components like the structure of the body, the power train and chassis must be designed taking into account the static and dynamic stiffness requirements, both localised as well as overall.
This is why conducting a proper analysis of the vibrations and frequency response of the Body in White (BiW) is essential during its development phase.
An NVH is carried out to improve the static and dynamic behaviour of the vehicle without significantly increasing its weight, which is a challenge for modern engineering, where increasing performance without adding mass is no longer an option. Current fuel efficiency and pollution standards require vehicle manufacturers to think twice before adding weight to a vehicle. Therefore, the optimisation of the design is essential in order to comply with requirements in terms of light-weight and NVH.
RESULTS
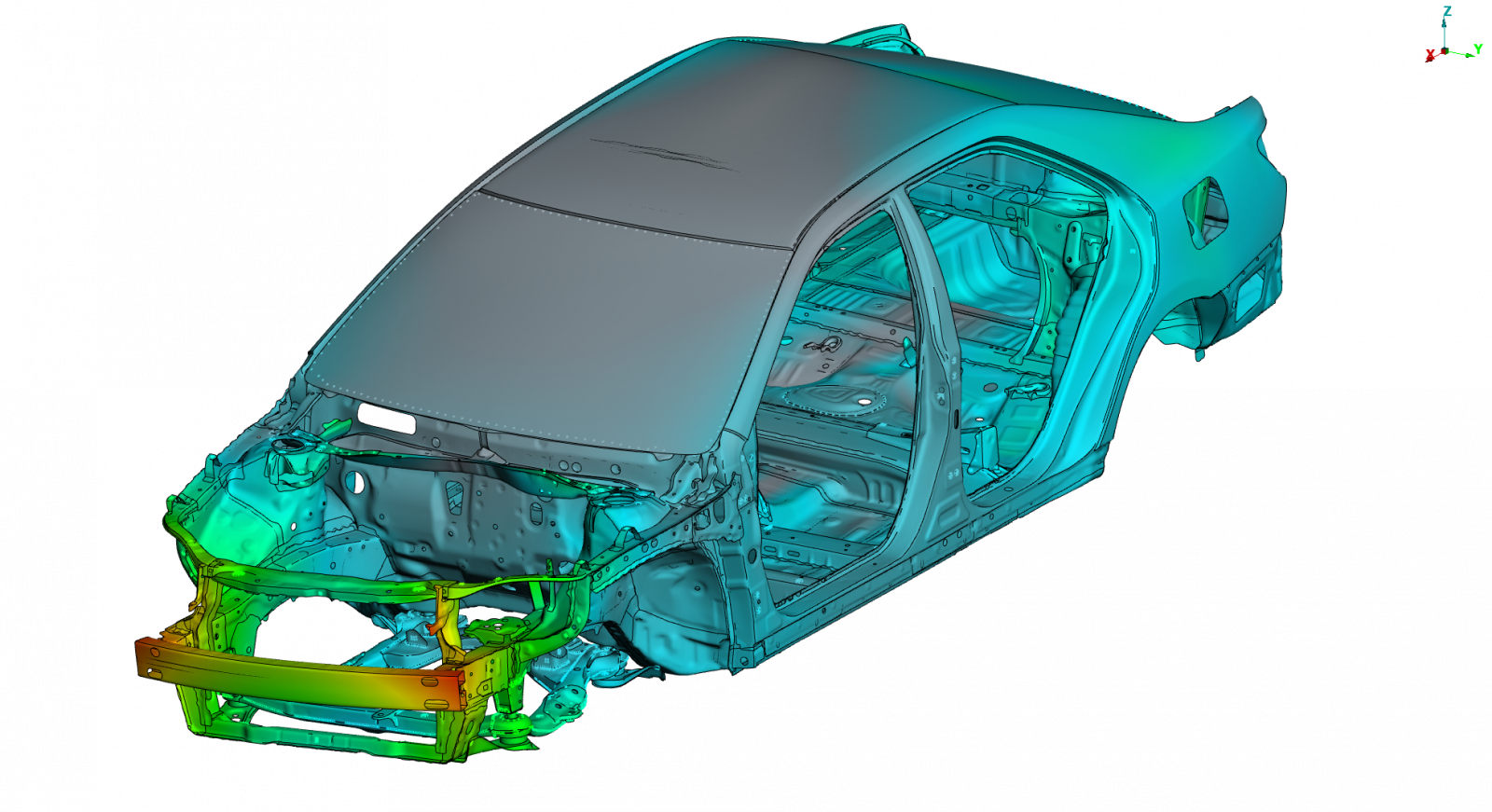
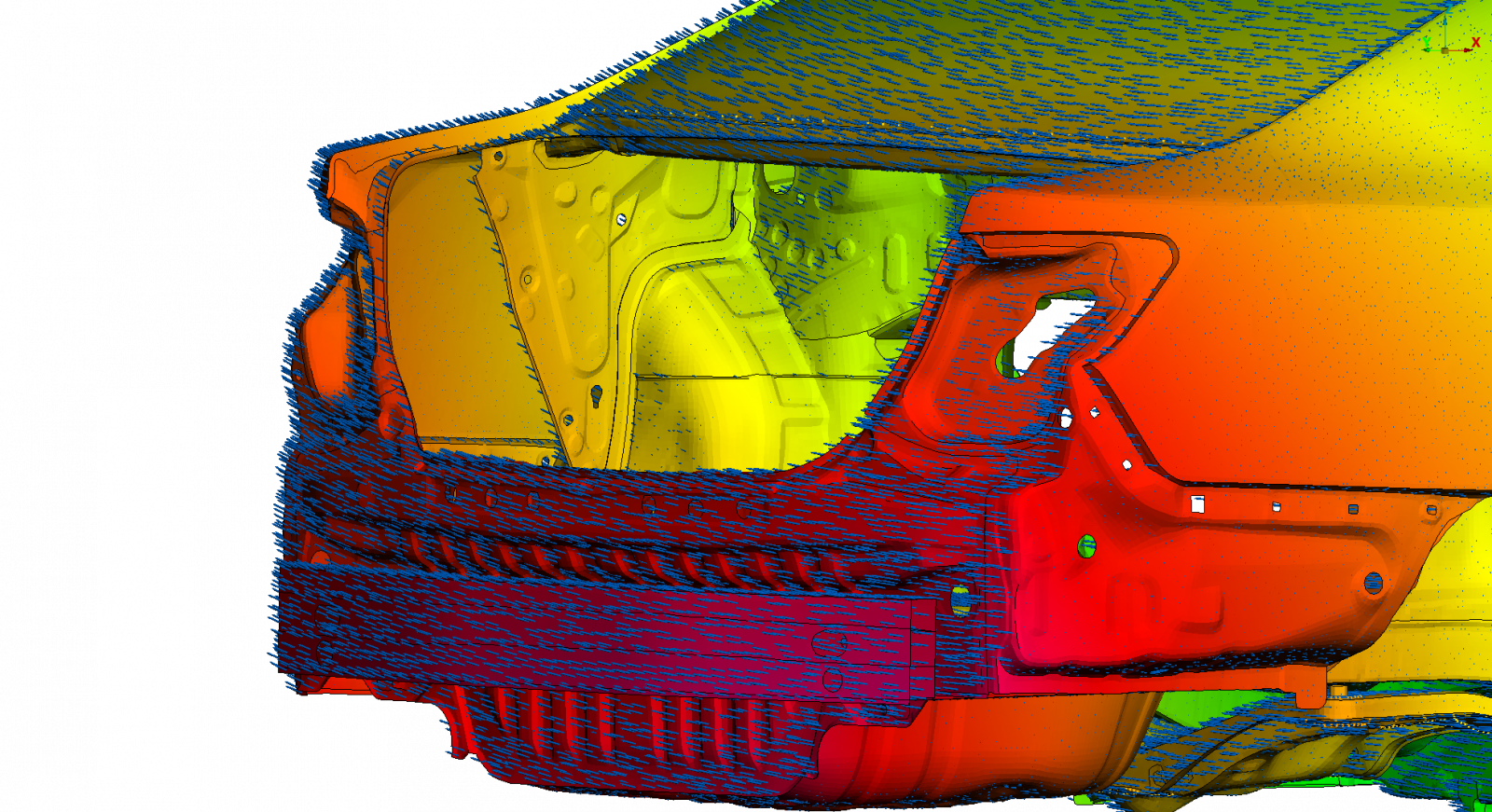
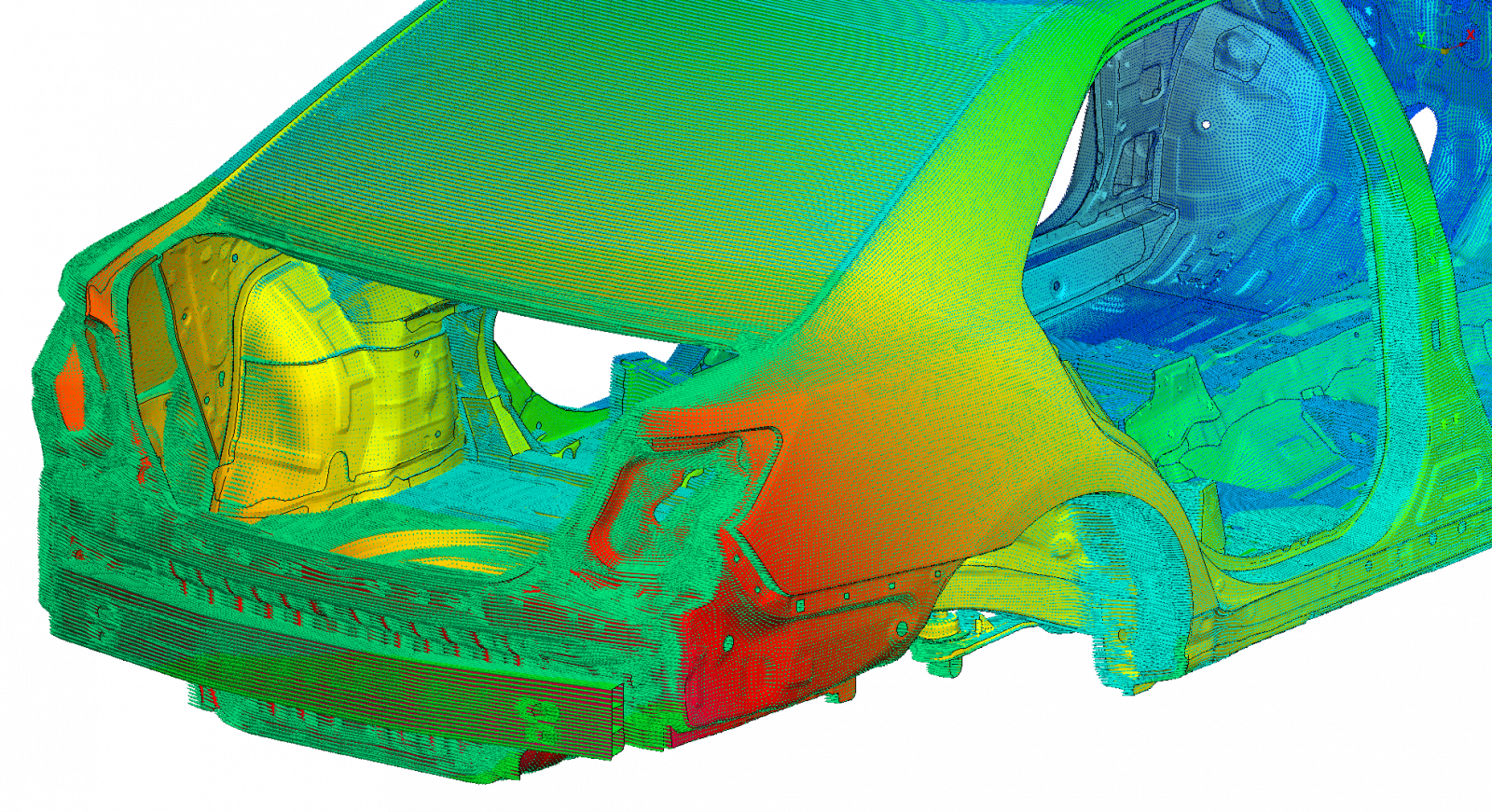
The FEM analysis that is carried out in the vehicle design phase allows understanding the overall static and dynamic stiffness behaviour. By identifying what components or parts affect performance, it is possible to, in concordance with other disciplines, quickly and effectively make design change decisions. This way, from a stiffness point of view, an optimal structural performance is ensured.
EXPERIENCE
Since 2016 SOLUTE has been continually collaborating on new developments with leading international car manufacturers (OEMs). Likewise, we also support suppliers of components to the automotive industry that need to comply with the high standards required by their customers.
Some of the important fields of NVH that SOLUTE has worked in are the study of the static stiffness of the Body in White (BiW), the assessment of the dynamic stiffness of the Body in White (BiW) and Trimmed Body (TB), as well as the analysis of the local vibration modes and the frequency response of the vehicle's local components.
The NVH assessment is carried out using CAE (Computer Assisted Engineering) software based on the Finite Elements Method (FEM). These programmes are usually commercial off the shelf (ANSA, NASTRAN, PAMCRASH, META, and ABAQUS)
METHODOLOGY
The NVH assessment is carried out using CAE (Computer Assisted Engineering) software based on the Finite Elements Method (FEM). These programmes are usually commercial off the shelf (ANSA, NASTRAN, PAMCRASH, META, and ABAQUS). Regardless of the software that is used, we always take into account the highest standards of practice in the simulation and the criteria in terms of evaluating the results, based on the experience accumulated by SOLUTE in recent years.
Depending on the level of complexity of the NVH assessment of a vehicle we can classify two major types of modelling: Body in White (BiW) and Trimmed Body (TB). In the first, a static stiffness analysis (torsional stiffness) and a dynamic stiffness analysis (modal analysis) are carried out on a model that only includes the body, the front bumper reinforcement, the sub-chassis, the front window and, in cases where the car is electric, the battery compartment as well. In the second type of modelling, the model is more complex and also includes moving parts (doors, hatch, hood, etc.), engine, steering components, seats and various masses to represent different components that are important for the dynamic and frequency response analysis that are carried out with the TB model.
The loads that are entered in the calculation will depend on the type of calculation. In the case of the static stiffness calculation, forces are applied to analyse torsional stiffness, as we would do for a test of this nature. On the other hand, BiW and TB modal analyses do not include boundary conditions; in other words, they are the free type. Finally, the frequency response analysis (FRF) of TB is normally carried out entering unit forces at important points of the car, taking into account the modal base obtained in the previous analysis.
Wind
Design, optimisation and certification of turbine components
Structural analysis of the components of a wind turbine to verify its integrity and survival to the historical performance of the intended operation.
Software
Continuous software integration and deployment
Software engineering branches focused on increasing the quality and frequency of the iteration in the developed solutions and on having greater control over all the stages that comprise the software's life cycle.