Design and certification of wind turbine towers
Timeline
2017-2023Sector
Renewable energy: wind and solarScope
Design and certification of wind turbine towersBACKGROUND
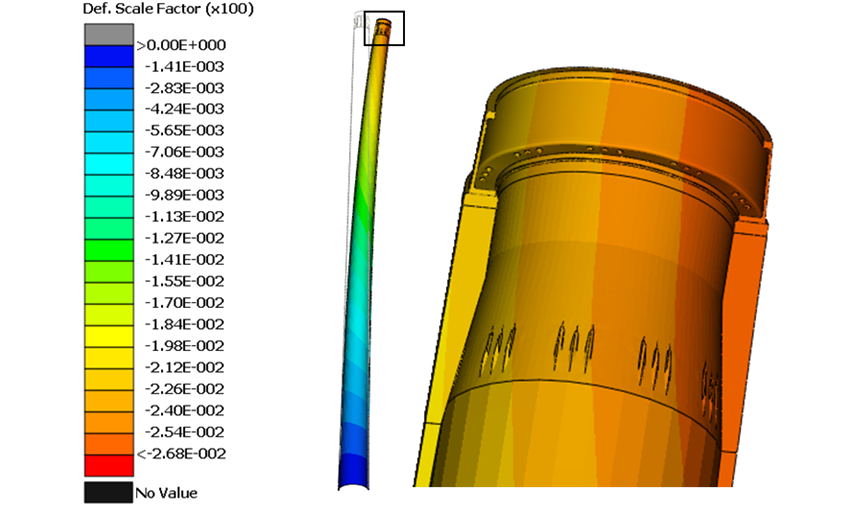
The tower is a critical element of the wind turbine structure and defining it is a task that SOLUTE has worked on while carrying out different projects involving the design and certification of varied types of towers for different customers.
The method used for towers structural calculation is focused on structurally comparing the different elements of steel, concrete or hybrid type towers, either in the ultimate limit state, of service or fatigue, as well as the special elements the foundation may have.
The tower is one of the most critical elements of a wind turbine, since its main function consists of transmitting the loads generated by the rotor to the foundation. Towers are especially sensitive to fatigue, where the constant oscillations of the turbine are able to dynamically excite the first modes of this element, which could generate undesired phenomena.
SOLUTE is capable of tackling the specialised civil engineering for the structural calculation based on our experience in designing different types of wind turbine towers: concrete, steel or hybrid. The methodology developed by SOLUTE is focused on obtaining the certification, agreed to in each case, with both the customer as well as the certifying body. This way, processes and standard documents are available, that may serve useful for streamlining the certification process, allowing us to complete the process within the normally strict established deadlines.
RESULTS
Optimum definition of all the tower elements through the documentation and appropriate drawings, in a manner that allows obtaining the certification from the accredited body.
EXPERIENCE
The main customers interested in these types of studies are wind turbine manufacturers as well as construction companies that have purchased wind turbine technology and need support in terms of defining the towers, or small engineering firms that have developed new types of towers and need to obtain a certification that will give them more visibility on the market.
In both cases, SOLUTE has recently carried out projects in which the foundation for the construction of wind turbines or its certification has been defined in due time and meeting the deadline.
The main standards used in the certification process primarily include IEC 61400 -1, Germanischer Lloyd (GL) Guidelines, Eurocode 2 (Design of concrete structures) and Eurocode 3 (Design of steel structures), and design codes such as CEB-FIP Model Code 1990 or 2010.
METHODOLOGY
The analysis of towers process is based on the industry standard regulation for wind turbines and structural calculation, both national as well as international. The main standards used in the certification process primarily include IEC 61400 -1, Germanischer Lloyd (GL) Guidelines, Eurocode 2 (Design of concrete structures) and Eurocode 3 (Design of steel structures), and design codes such as CEB-FIP Model Code 1990 or 2010. These regulations are complemented with numerous related publications, following the state of the art of the sector.
The work tools that are used for the calculation models include specialised FEM software such as SAP2000 (CSI) as well as sectional calculation software FAGUS (CUBUS). Regarding the analytical post-processing of the results of the modelling and data processing, we have developed our own tools in Microsoft Excel.
The methodology is focused on checking the overall operation of the structure and defining the specific elements to ensure this behaviour is real. The steps followed may be grouped in:
• Ultimate limit state, service and fatigue analysis of the general elements of the structure.
• Definition and structural analysis of special elements such as openings for cables or doors.
• Verification of the different connections between elements that make up the tower, using clamps or mortar.
The process entails drafting documentation based on the requirements set by the certifying body, mainly comprised of documents that back up the calculations that are made and drawings with the definition of the geometry, armature and other elements that may be present in the structure.
Others
Artificial Intelligence
Discipline based on the construction of computational artefacts that learn from experience through data use and that is applied to a variety of problems.
Others
Hydraulics: turbomachines
Turbomachinery is present in many engineering sectors, including electrical power generation, using gas or wind turbines, propulsion in air vehicles or different industrial processes with turbo-compressors and/or hydraulic pumps.