Structural systems design for PV plants
Timeline
2006-2023Sector
Renewable energies: wind and solarScope
Solar energy: structural systems design for PV plantsBACKGROUND
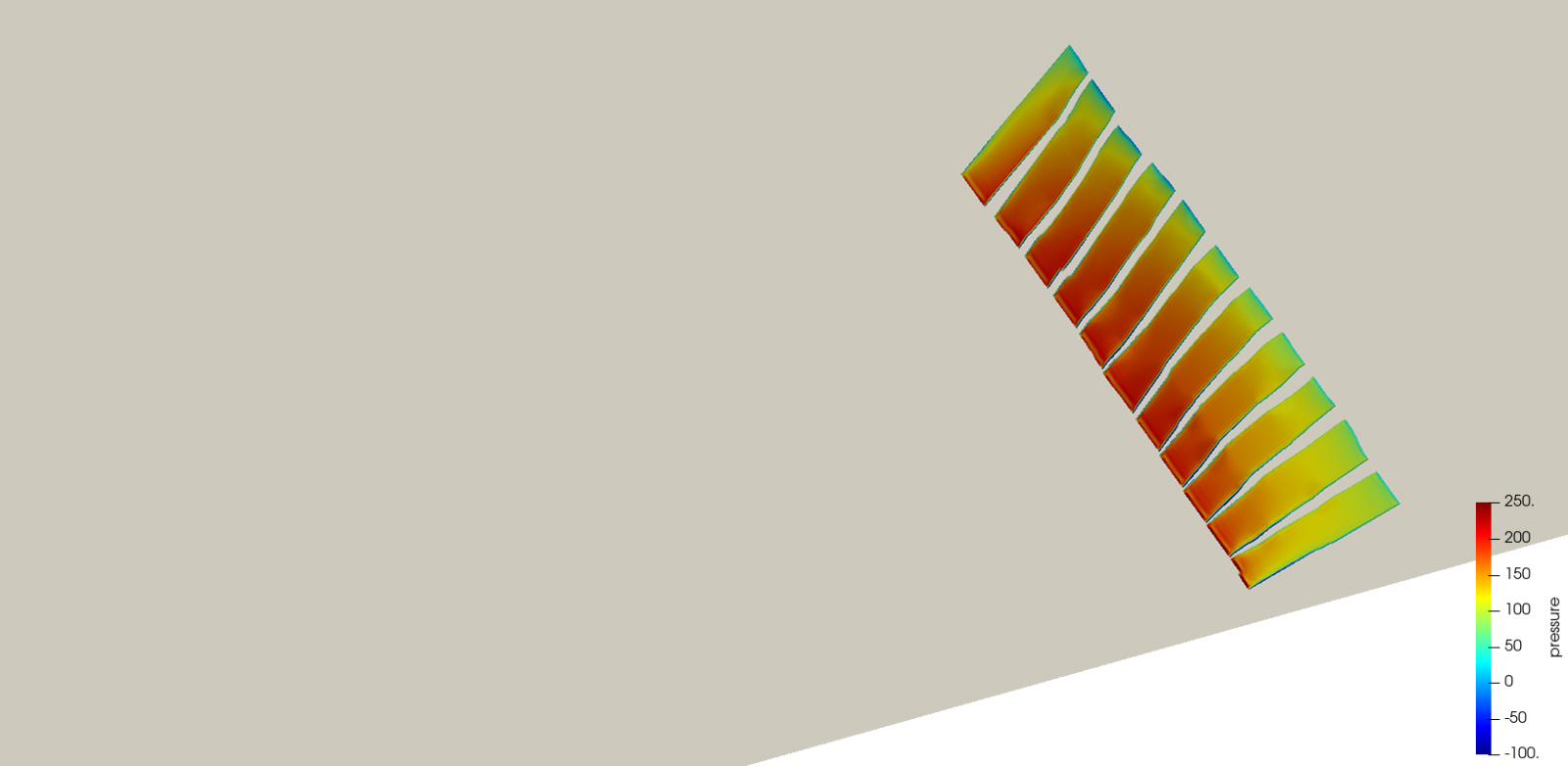
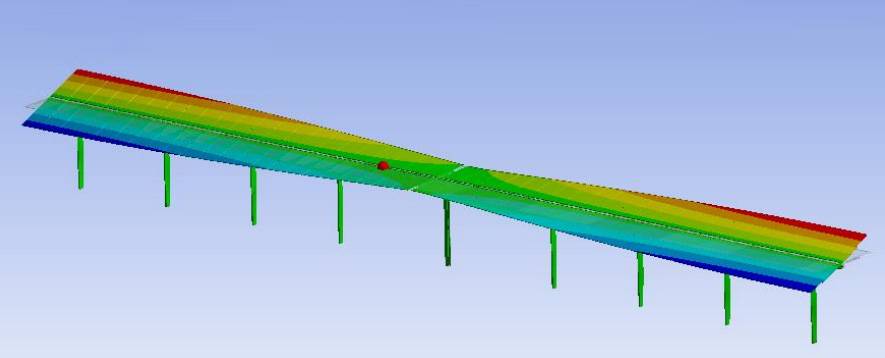
Solar power generation plants using PV panels require a structural calculation for the most demanding actions such as wind and earthquakes, depending on the case. Undertaking the design of these critical scenarios sometimes requires a multidisciplinary approach, as in the case of the interaction between wind and the structure. In these cases, computational fluid dynamics CFD and structural simulation using Finite Elements Modelling (FEM) must interact in terms of exchanging information, which requires determining a specific methodology. In these approaches, SOLUTE contributes their knowledge in these fields to carry out the analysis in the design phases of these systems. Other aspects that require a more conventional analysis are the analysis of the joints between components, support structures and anchoring to the ground, among others.
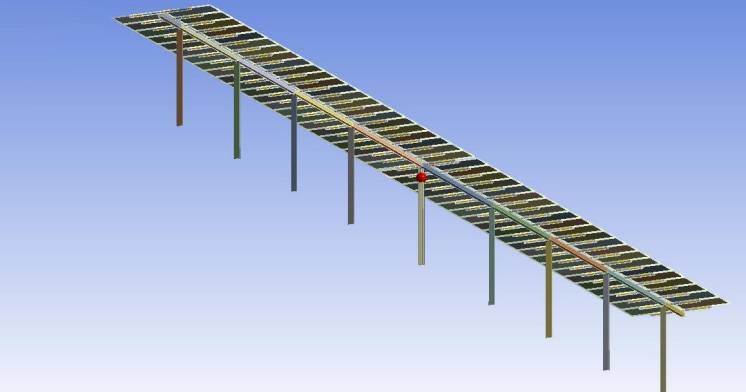
Photovoltaic plants, as renewable energy sources, are experiencing constant growth and require an engineering task that is highly focused on obtaining structural systems that meet requirements, are cost effective and with a maintenance that is optimal.
The aim is to fully define the mechanical support structure of the photovoltaic plants, the anchoring to the ground where they are installed as well as the joints between components, always in accordance with the applicable regulations of each country to guarantee a useful and extensive service life that minimises the costs associated with Operation and Maintenance (O&M).
RESULTS
The analysis is specified in a design that can be realised in 3D geometries or construction plans, if required, in addition to a detailed structural calculation report.
EXPERIENCE
Since its establishment in 2006, SOLUTE has gained extensive experience in structural calculations, which it has specifically applied to the structural systems of photovoltaic plants. To carry out these types of analyses, different tools, methodologies and approaches are used, which together with SOLUTE's mastery and know-how, allows us to propose and define the most suitable solution in each case.
SOLUTE offers the ability to carry out a fluid dynamic analysis with 3D and 2D models, including the interaction with the structural response.
METHODOLOGY
The first step is to conduct an in-depth study of the regulation of pertinent actions and after evaluating the customer's constraints, carry out a first definition of the structure, using a combination of analytical calculation and finite elements modelling (FEM). Special attention is given to welded and bolted joints calculations or any other system used for fastening the panels to the structure. Likewise, if the scope covers the anchoring of the substructure to the ground, this aspect is addressed in the first phases. This process iteratively evolves in the next steps until an optimum solution is found.
In cases where the study references the actions of the wind and a simplification of the situations to be addressed is not available, SOLUTE offers the ability to carry out a fluid dynamic analysis with 3D and 2D models, including the interaction with the structural response. This approach is the most realistic approximation but due to the higher computational cost, we must decide on the optimal strategy according to the circumstance.
These methods of analysis can be adapted to different types of requirements, from pre-designs and review of existing designs to others that are completely new.
Eólica
Edificios inteligentes y smart control del consumo energía
Mejora de la eficiencia de los edificios mediante estrategias de automatización y la implementación de gestión inteligente en la demanda de la energía.
Automoción
Sensórica
El análisis de la sensórica del automóvil contribuye a optimizar las señales recibidas por los ordenadores del vehículo, que le llegan a través de los distintos sensores dispuestos, para activar su función de manera correcta y en el momento adecuado.