Air conditioning for working safety in industrial environments
Period
2017-2022Sector
AutomotiveFluid dynamics: air conditioning systems in vehicles
Air conditioning for working safety in industrial environmentsBACKGROUND
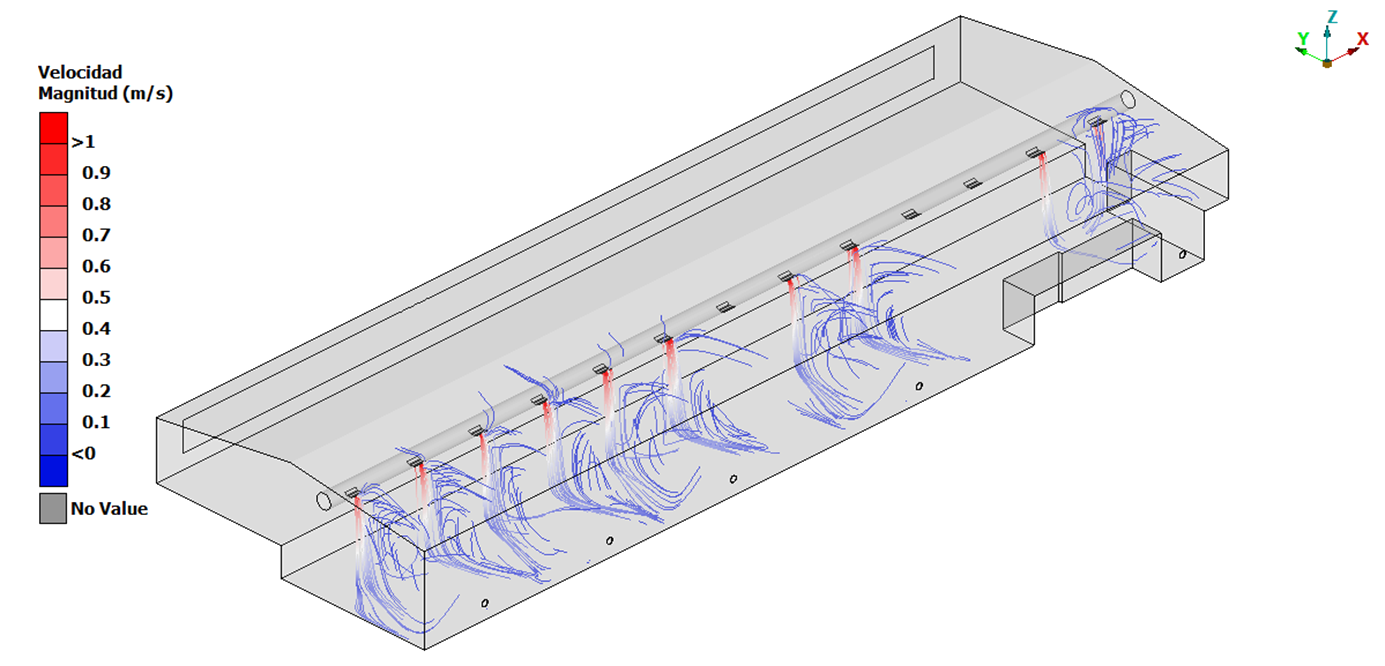
Study and optimisation of the air conditions in industrial environments to guarantee compliance with the current occupational risk prevention regulation.
Using CFD (Computational Fluid Dynamics) tools we are able to predict the behaviour of the air in working environments, especially focused on the removal of contaminants such as dust generated by the machining of metal parts. CFD calculations allow establishing certain working conditions in terms of the ideal temperature, pressure, humidity or suspended particles in the most efficient manner possible.
Working environments must meet very strict environmental requirements in order to provide healthy conditions for workers. In industrial environments, meeting requirements is more difficult for several reasons. First, work usually takes place in large spaces such as industrial buildings with machines that emit heat into the environment and therefore, controlling the temperature in these spaces is difficult. Industrial processes usually generate waste that remains suspended in the air and is harmful to human health.
Different measures are available to achieve an ideal air space in working environments and thanks to the use of CFD tools, we are able to calculate and predict the success of the implementation of these measures. This is how we can optimise the development of the measures and their cost.
RESULTS
For results, a report is generated with all the data obtained in the original HVAC system and in the different proposals, and the most suitable option between them is selected based on the defined criteria.
The tasks of simulation and analysis of your results allow, in a very dynamic way, adopting alternatives to the design or concept when the results are unsatisfactory, as well as the optimisation of the geometries. This way, studies are provided with great added value in terms of the thermal and kinematic behaviour of the air flow in working environments, thus guaranteeing the established requirements are met.
EXPERIENCE
SOLUTE has carried out numerous HVAC simulations for different customers in the automotive sector. Numerous cab air conditioning development phases have been carried out in cars and this methodology has also been applied in buses. These phases have ranged from evaluating the comfort of occupants to de-icing and defogging systems to ensure visibility through the wind shields.
To carry out these types of studies, SOLUTE relies on their extensive experience and know-how in CFD fluid dynamics and simulation software, which it has been applying to problems of very different natures.
After a first study of the state of the art and the set objectives during the development of the HVAC system, models are created based on the geometry and on the case study.
METHODOLOGY
The analysis is carried out with CFD (Computational Fluid Dynamics) tools, using the Finite Volumes Method (FVM) or the Finite Elements Method (FEM), depending on the solver that is chosen. To carry out these calculations, commercial codes (ANSYS, ALTAR) as well as free use codes (OpenFOAM) are used, over which, even with differences in their origin, good practices in modelling standards prevail as well as the criteria of expert analysts and the basis of extensive experience.
After a first study of the state of the art and the set objectives during the development of the HVAC system, models are created based on the geometry and on the case study. This way, the intent is to simplify and individualise the model, so that we can reach a compromise between the accuracy of the results and the computational load. In most situations, stationary simulations RANS (Raynolds-Averaged Navier Stokes) or their transitory variable URANS (unsteady RANS) will be used and sometimes, more expensive and accurate simulations may need to be used such as LES (Large Eddy Simulation).
Based on a scenario that contemplates all the physics and all the constraints inherent to the analysis that is to be addressed (for which we will need to properly define the properties of the fluid, its domain and contour conditions), we can calculate and determine the desired aspects of the model such as distributions of pressure or speeds, the air flow or temperature.
Based on the results that are obtained, the validation of the original HVAC system is studied in accordance with the current regulation. In the case of Spain, the Occupational Risk Prevention Law of 1995 and subsequent updates in the form of royal decrees is applicable, or ISO 45001 on Safety and Health at the workplace.
In addition to a quantitative result, the tools that are used allow analysing the qualitative behaviour of the evaluated systems, detecting the areas that cause undesired operations and the regions that have potential for improvement. This way, once the first series of simulations are completed, proposals for improvement are made and the process is repeated until the optimum solution is reached. To accomplish this it is essential that we have the skills and know-how of engineers who are experts in aerodynamics and fluid mechanics, since a proper interpretation of the results and identification of possible solutions requires knowing the behaviour of the fluid described by the Navier-Stokes equations, as well as the nature of all its components.
Automotive
HVAC
Capability of guaranteeing a proper heating, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC) in vehicles used for transport, of both the cabs as well as the compartments where the payload is carried for different reasons, such as conservation or passenger comfort.
Wind
Life extension evaluation of towers and foundations
This competency allows extending the functional duration of turbine components and thus obtains a greater performance from the installed wind turbines.